While how LLMs work may be elusive to many developers, how LLM apps work is not - they essentially involve a series of calls to external services such as LLMs/databases/search engines, or intermediate data processing, all glued together. Thus LLM apps are merely Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) of function calls. These DAGs are flows in prompt flow.
Flows#
A flow in prompt flow is a DAG of functions (we call them tools). These functions/tools connected via input/output dependencies and executed based on the topology by prompt flow executor.
A flow is represented as a YAML file and can be visualized with our Prompt flow for VS Code extension. Here is an example:
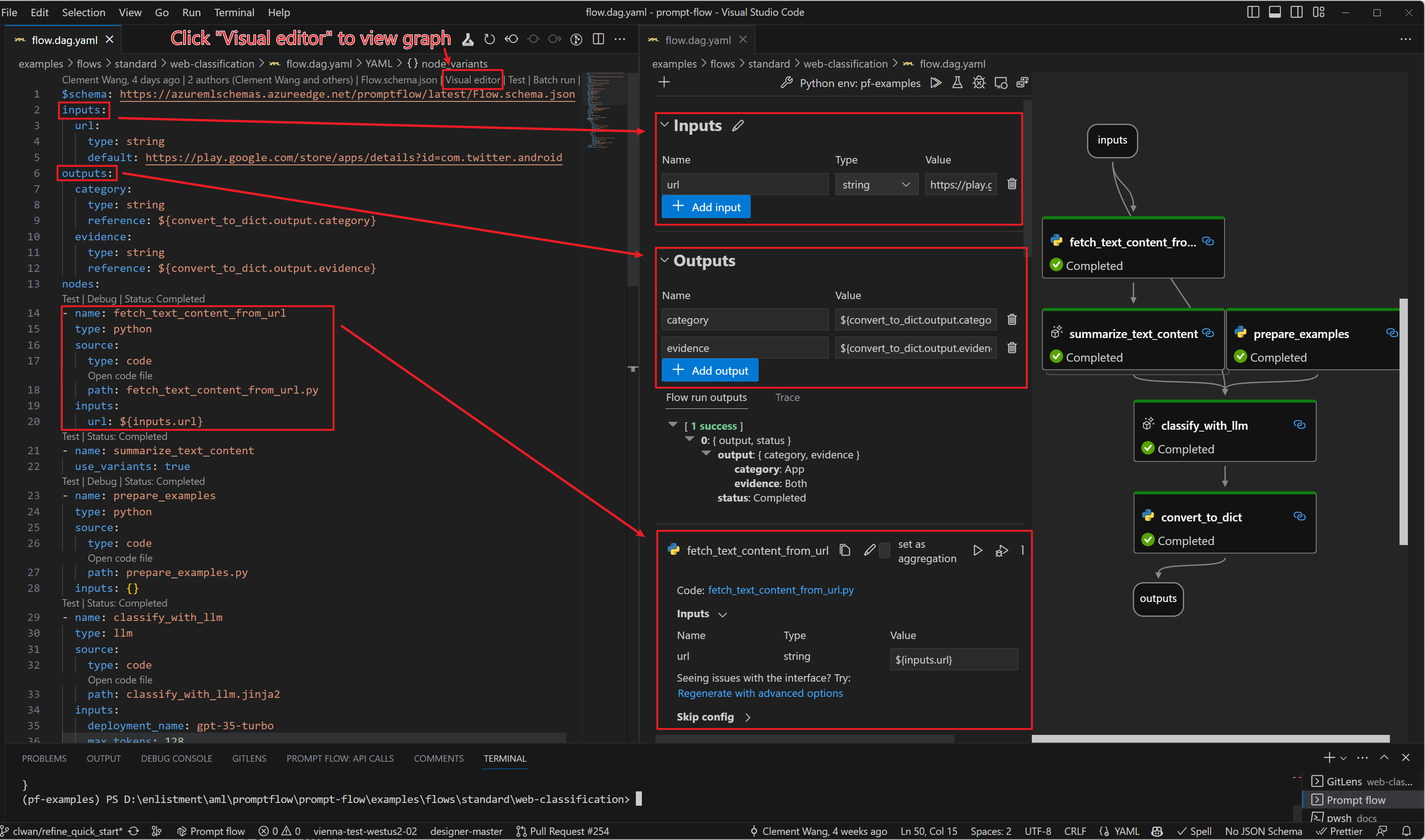
Flow types#
Prompt flow has three flow types:
Standard flow and Chat flow: these two are for you to develop your LLM application. The primary difference between the two lies in the additional support provided by the “Chat Flow” for chat applications. For instance, you can define chat_history, chat_input, and chat_output for your flow. The prompt flow, in turn, will offer a chat-like experience (including conversation history) during the development of the flow. Moreover, it also provides a sample chat application for deployment purposes.
Evaluation flow is for you to test/evaluate the quality of your LLM application (standard/chat flow). It usually run on the outputs of standard/chat flow, and compute some metrics that can be used to determine whether the standard/chat flow performs well. E.g. is the answer accurate? is the answer fact-based?
When to use standard flow vs. chat flow?#
As a general guideline, if you are building a chatbot that needs to maintain conversation history, try chat flow. In most other cases, standard flow should serve your needs.
Our examples should also give you an idea when to use what: